
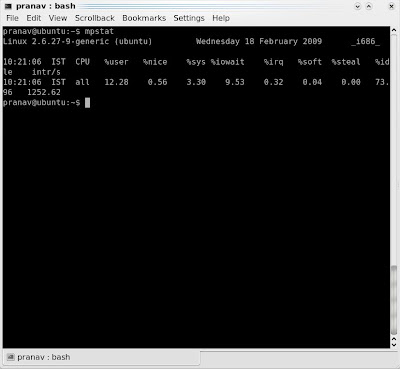
This command provides network activity statistics. For example, to view memory usage for buffer cache, use following command − By default, sar displays memory usage for all memory types, but you can specify a specific memory type using "-B" option. "-r" option specifies that we want to see memory statistics. This command provides memory utilization statistics. For example, to view CPU usage for CPU 0, use following command − By default, sar displays CPU usage for all CPUs, but you can specify a specific CPU using "-P" option. "-u" option specifies that we want to see CPU statistics. This command provides CPU utilization statistics. Now that we have an overview of Sysstat utilities, let's explore some of top commands for performance monitoring.

Top Sysstat utilities commands for performance monitoring However, if you do need to install them, you can use following commands −įor Debian-based distributions − sudo apt-get install sysstatįor Red Hat-based distributions − sudo yum install sysstat Sysstat utilities are typically included in most Linux distributions, so you may not need to install them manually. Installation of Sysstat Utilitiesīefore we dive into Sysstat utilities commands, let's first discuss how to install them. In this article, we will explore 20 useful commands of Sysstat utilities for Linux performance monitoring. Sysstat utilities are a collection of tools that provide detailed system performance information, including CPU utilization, memory usage, disk activity, and network activity. There are a lot of tools available for this purpose, and one of most widely used is Sysstat utilities. In world of Linux system administration, performance monitoring is an important task.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
